For any online store, tracking competitors’ product prices on Google Shopping should be one of the key strategic priorities. Many businesses get puzzled when it comes to finding effective ways to compare Google Shopping prices to their competitors. In this blog post, we’ll cover the primary tactics and solutions for tracking competitors’ prices on Google Shopping. Also, we’ll go through a case study we’ve run recently on competitor price tracking and monitoring—some exciting insights there!
Table of Contents
How to Do Google Shopping Price Comparison
Google Shopping price comparison for competitors’ products can provide you with valuable data. You can use it to smartly tweak your price and bidding strategies in an instant.
Getting competitors’ product price data can involve different actions, like
- setting up price alerts
- using third-party tools
- using API, etc.
For each business, it boils down to an individual choice of solutions and tools for tracking prices on Google Shopping. All stores are different in size and business goals. Plus, there are other factors that impact the final decision of choosing product price tracking solutions like
- how large and diverse the shop’s stock is
- what target audiences they are reaching out to
- their location
- how competent their dev team is, etc.
So how to track prices on Google Shopping the best way possible? Let’s take a look at the list of solutions you can use to monitor competitors’ product prices on Google Shopping.
1. Benchmark Against Competitors’ Prices on Google Shopping Ads
Benchmarking against competitors’ prices on Google Shopping ads is a great way of understanding if your pricing and bidding strategies either work or need optimisation. You’ll be able to see how other businesses are pricing the same products that you sell by getting a click-weighted average price for each product. This data can be useful for understanding what works well for your competitors in terms of the pricing approach that triggers clicks for this or that product. Currently, this functionality is in beta.
There are three functionalities available for benchmarking against competitors’ prices for Google Shopping ads.
- Average product price shows the price of a product when your ad appeared to the audience or when the ad competed in an auction.
- Benchmark product price. This is the average click-weighted price for a product across all merchants who push Shopping ads for that product.
- Benchmark product price difference is the percentage difference between your product’s average price and the associated benchmark product price.
For more details on product price benchmarking for Google Shopping ads, check this article.
2. Use an API for Product Price Monitoring on Google Shopping
You can use an API for tracking Google Shopping product prices in your competitors’ offerings. The basic approach for monitoring the product prices of the competitors boils down to setting up a web scraping API that recurrently tracks SERP results and grabs the data and information you need. There are two main benefits of using SERP scraping API for product tracking.
- SERP scraping can help you filter out the results and leave only those related to Google Shopping—basically, it becomes a focused Google Shopping API price comparison tool.
- With SERP scraping API, you can get data on any attributes like ID, product type, price, etc.
The product data you receive can be processed further with automated scripts that neatly convert it into reports. You can also ask your dev team to set up a Google Shopping price alert for specific attributes like product price, store (merchant), etc.
Altogether SERP scraping looks great but setting it up correctly demands tech-savvy expertise, so you could go for the following options:
- get a highly competent in-house dev team
- get devs one on the outsourcing
- subscribe to one of the ready-to-use Google search API scraping services (which would still demand somewhat expertise from your in-house devs).
3. Use Ready-Made Tools for Google Shopping Price Tracking
Using product price trackers is another way to track competitors’ Google Shopping prices. There are quite a number of product price trackers for Google Shopping available out there. The benefits of using a ready-made tool for monitoring product prices on Google Shopping are the following.
- Compared to raw SERP API scraping, such solutions don’t need extra effort from the dev team to tune up because the tool you’re getting already serves the purpose—everything is already set up and ready to get fired up.
- Out-of-the-box Google Shopping price trackers come with a user-friendly UI and useful features that are easy to understand and use.
- Ready solutions for Google Shopping optimization, including those focused on price monitoring, offer great automation features.
4. Directly Compare Product Prices in Google Shopping
Google provides their users with a simple yet useful feature for tracking drops in product prices—something that you can call a Google Shopping price tracker. This feature can be extremely handy if
- you and your competitors sell products within a limited geographical location—you can choose nearby competitors’ shops and start tracking prices for precise products that you all sell
- you’re trying to spot price drops in competitors’ offerings for an exact product or a set of products—this may work even for larger markets and broader geolocations.
Google’s price tracking feature in the Shopping tab is meant predominantly for consumers, not businesses and merchants. It means the price tracking feature can be set up in Google’s user interface only. If you want to use this feature as the only tool for Google Shopping price monitoring, there are some downsides associated with this solution, including the following:
- you’ll have to go through each of the product price alerts on Google Shopping manually
- you’ll be receiving price drop notifications on your Google app (US only) on mobile or in Chrome browser, which is not very convenient—you’ll have to manually set up a database for the price drops (e.g. a spreadsheet) and copy-paste the numbers you get for each product.
For larger online retailers, price drop monitoring on Google Shopping may also be a go-to solution if they are tracking something definitive like an exact model—or a number of models—of products from competitors that they are trying to win over.
For example, if you’re a member of a marketing team, this feature can notify you right away if your competitor drops the prices of their products. Just remember that price drop monitoring with Google Shopping UI will demand a lot of manual action if you are going to process large chunks of product price information. Trying to track prices for hundreds of products with the Price track feature may not work for you.
Learn more about setting up price drop monitoring here.
Analysis of Competing Product Prices on Google Shopping [BrightBid Data Study]
Using our AI engine for Google Shopping—Bidbrain—we have analyzed 150,000 products in online stores across different industries. For 6,500 products, we were able to get price comparison data on Google Shopping.
We tried to find out what pricing approach works best sales-wise. Our data analysts studied the product prices and found out the following.
Comparison of Product Price Levels on Google Shopping
Out of 6,500 products, we got the following statistics for the overall pricing balance between the stores.
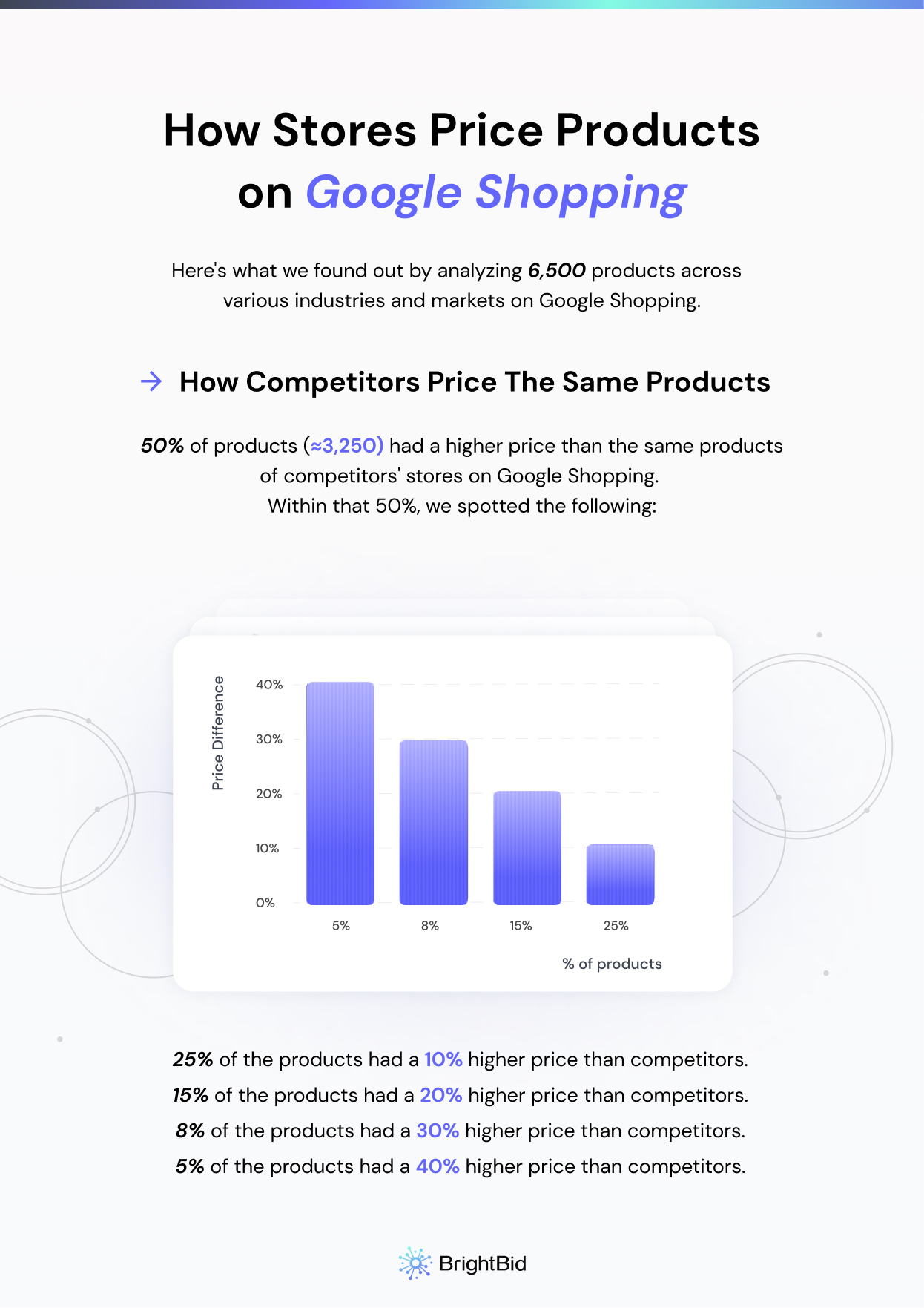
50% of products (≈3,250) had a higher price than the same products of competitors’ stores on Google Shopping. Within that 50%, we spotted the following.
- 25% of the products had a 10% higher price than competitors.
- 15% of the products had a 20% higher price than competitors.
- 8% of the products had a 30% higher price than competitors.
- 5% of the products had a 40% higher price than competitors.
Looking at the numbers, the first question that you might ask would be “Why do 50% of stores put higher prices?”. Well, the customer journey is a complicated thing. Many customers are searching for more expensive products because, in their opinion, “cheap means bad” or they are just looking for obvious added value, etc. In some cases, it is convenient to have higher prices than that of the competitors. So, the decision to buy from an exact store that product is impacted by two types of factors that are tied to each other.
- Psychological factors. These include things like feeling comfortable with buying products from a favourite shop, trusting a store because it has a reputed brand, buying a product with a higher price because of BOGO included, sticking with a sentiment that more expensive means higher quality, and even making a purchase because of how appealing a store’s UI is.
- Marketing factors. Basically, these show how well you’re doing your job at every stage of the marketing funnel—from attracting customers at the awareness stage to getting returning customers and brand advocates and making use of remarketing.
Outside psychological factors, some shops may choose to sell products at higher prices because of a store’s higher overhead costs. Whatever the reason for pricing products higher, it is important for the store to make sure that customers understand why they are paying more. The store should be clear that the higher price is due to the extra value they are getting from the product or service. Otherwise, customers may feel like they are being taken advantage of. They may also feel put off from returning to the store in the future.
Get the Most Out Of Your Shopping Ads
How Product Prices Affect Conversion Rates on Google Shopping
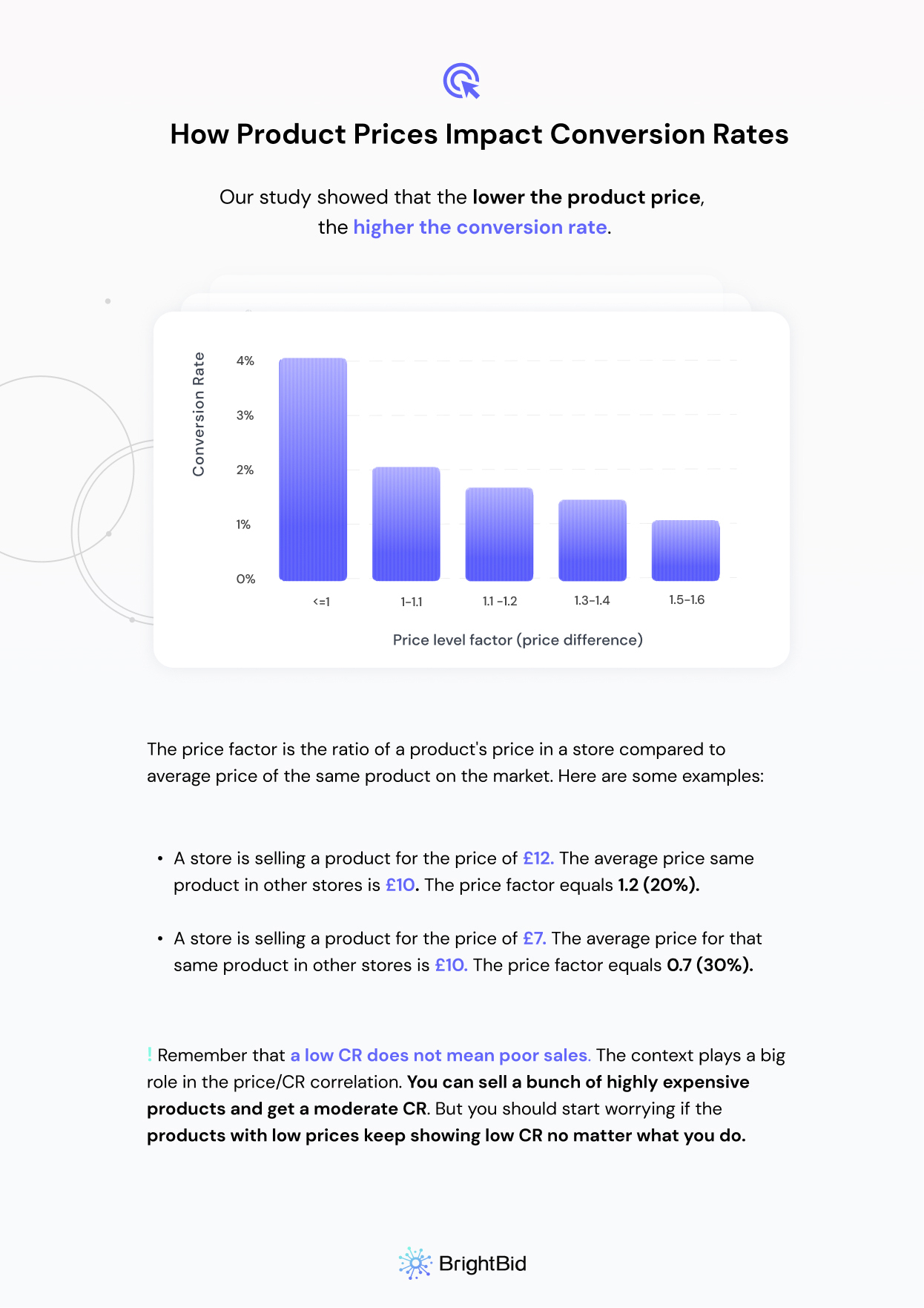
We also looked at the correlation between pricing and conversion rates. In general, it turned out that the lower the product price, the higher the conversion rate is, which proves that there are also target audiences that are looking for affordable purchases. This might not come as a big surprise. However, any store should remember that there are indirect factors that influence the success of the price/conversion relationship. Just putting up a price lower than that of the competitor is not enough. Pay attention to the following.
- Timing. Some products are selling just fine with their prices being unchanged for some time, the others need multiple tweaks at times. For example, you’re getting rid of poor-selling products, trying to win over the competition for customers’ attention during a sales season, or you noticed that your competitor is not very smart at pricing their products, e.g. their prices are higher than average.
- Consistency of the product offerings. Your product offerings must always be clear as day—from consistent and understandable product titles and descriptions, and shipping and return policies to the most seemingly insignificant information like size, colour, material, etc.
It is also important to remember that a low CR does not mean poor sales. The context plays a big role in this case. For example, you can sell a bunch of costly products and still hit the target numbers with a moderate CR. But you should start worrying if the products with low prices in your stock keep showing low CR no matter what you do.
Check the full stats for the price/CR correlation below.
- Products with a price level factor <=1, had an average CR of 4%.
- Products with a price level factor between 1-1.1, had an average CR of 2%.
- Products with a price level factor between 1.1-1.2, had an average CR of 1.7%.
- Products with a price level factor between 1.3-1.4, had an average CR of 1.2%.
- Products with a price level factor between 1.5-1.6, had an average CR of 1%.
What is the price factor, you may ask? The price factor is the ratio of a product’s price in a store compared to the average price of the same product on the market. Here are some examples.
- A store is selling a product for the price of £12. The average price for that exact product in other stores is £10. The price factor equals 1.2 (20%).
- A store is selling a product for the price of £7. The average price for that exact product in other stores is £10. The price factor equals 0.7 (30%).

How to Use Price Comparison Data to Improve Performance on Google Shopping
By adding the price comparison data to your product feed, you can use the price factor to set more granular bids depending on how likely a product is to convert compared to the product prices of your competitors at a given moment. The most common way to do that is to group price comparison levels into a custom label. Check some examples below.
- For all products with a price 5% below the average price, set Custom label low-priced.
- For all products with a price +-5% of the average price, set Custom label mid-priced.
- For all products with a price 5% above the average price, set Custom label high-priced.
With the needed data on your hands, you can
- either set bids depending on a custom label manually
- or create different campaigns for different groups and weigh your budget against the products most likely to convert (low-priced).
Another solution is to use automated bidding. For example, machine learning is used in Bidbrain’s automated bidding to forecast the most effective bid to assist in ad spend return optimisation for each product in a store’s stock. Bidbrain’s AI is always improving as more data is fed into it. Get in touch to learn how Bidbrain can help you use price data to perform better on Google Shopping.
Final Thoughts
When pricing products, it is important to consider all of the factors that impact the success of your online store. Some stores are doing great by going with low product prices. The others achieve good results by selling solely expensive stuff. There are also those shops that mix different pricing approaches and get the conversion rates they aim at. All these businesses have one thing in common—a coherent approach towards product pricing. They know their market niche and competitors, they understand their target audiences and existing customers, and they realise what price benchmarking tools work exactly for them.

How to Use Price Comparison in Feed Optimization



 ” />
” />
 ” />
” />
 ” />
” />
